Labrador Feeding Chart by Age A Comprehensive Guide to Nutrition for Healthy Growth and Lifelong Wellness
Proper nutrition is the cornerstone of long-term health and vitality for any dog, but it holds particular importance for Labrador Retrievers. Ensuring that your Lab receives the right balance of nutrients from an early age can significantly influence their overall well-being, development, and longevity. A Labrador feeding chart by age is an essential tool in this regard, providing detailed guidelines on the appropriate amounts and types of food needed as your dog grows. This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions about feeding your Labrador, thereby promoting their optimal health throughout all stages of life.
Nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining a dog’s health, energy levels, and immune function. For Labradors, a breed known for their high energy and enthusiasm, proper nutrition is essential. Feeding your Labrador a balanced diet helps in maintaining a healthy weight, supporting their musculoskeletal development, and preventing common health issues such as obesity, diabetes, and joint problems. Quality nutrition also contributes to a shiny coat, healthy skin, and robust digestive health.
Puppies, in particular, require a diet that supports rapid growth and development. During the first year of life, a Labrador puppy’s nutritional needs are significantly different from those of an adult dog. They need more proteins and fats to fuel their growth and development, along with essential vitamins and minerals to support bone and muscle formation.
Labradors have specific dietary requirements that set them apart from other breeds. They are genetically predisposed to gain weight easily, making weight management a critical aspect of their care. This propensity for weight gain means that Labradors are at a higher risk for obesity-related conditions, including arthritis, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Moreover, Labradors are known for their voracious appetites, which can make portion control challenging. They often do not self-regulate their food intake, leading to overfeeding if not carefully managed. It is essential to monitor their diet closely and provide meals that meet their nutritional needs without exceeding their caloric requirements.
In addition to weight management, Labradors benefit from diets rich in Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, which support joint health and reduce inflammation. A balanced diet that includes high-quality proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of vitamins and minerals will help ensure that your Labrador remains healthy and active throughout their life.
Understanding Labrador Retrievers’ Nutritional Needs
Labrador Retrievers are beloved for their friendly disposition, intelligence, and boundless energy. However, their nutritional needs are unique and require careful management to ensure they remain healthy and active throughout their lives. This section delves into the genetic predispositions that influence their dietary requirements and provides general nutritional guidelines to help you make informed decisions for your Lab’s diet.
Genetic Predispositions and Weight Management
Labradors’ Tendency to Gain Weight
Labrador Retrievers are genetically predisposed to gain weight more easily than many other breeds. This tendency is partly due to their insatiable appetite and a gene mutation known as POMC (pro-opiomelanocortin). This gene mutation affects the brain’s ability to regulate appetite and feeling of fullness, making Labradors more prone to overeating. As a result, Labs often continue to feel hungry even after consuming an adequate amount of food.
Their love for food, combined with a lack of self-regulation, makes portion control crucial. Without careful management, Labradors can quickly become overweight, which significantly impacts their health and quality of life. Owners must be vigilant about feeding practices and avoid giving in to their pet’s pleading eyes and apparent hunger.
Long-Term Health Issues Related to Obesity
Obesity is a serious health concern for Labrador Retrievers, leading to a range of long-term health problems. Overweight Labs are at a higher risk for developing conditions such as:
- Arthritis and Joint Issues: Excess weight puts additional stress on joints, exacerbating conditions like hip dysplasia and arthritis, which are already common in the breed.
- Diabetes: Obesity increases the risk of insulin resistance, leading to diabetes mellitus, a condition that requires lifelong management.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Overweight dogs are more prone to heart conditions due to the extra burden on their cardiovascular system.
- Reduced Mobility and Activity Levels: Obesity can limit a dog’s mobility, reducing their ability to exercise and play, which further contributes to weight gain and a decline in overall health.
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for preventing these issues and ensuring your Labrador leads a long, healthy, and active life.
General Nutritional Guidelines for Puppies
Importance of a Balanced Diet for Growth and Development
A balanced diet is fundamental for the proper growth and development of Labrador puppies. During their first year of life, puppies undergo rapid growth, requiring a higher intake of specific nutrients to support their developing bodies. Proper nutrition during this critical period sets the foundation for a healthy adulthood.
Key Nutritional Components for Labrador Puppies:
- Proteins: Essential for muscle development and overall growth. Puppies need high-quality protein sources to build strong muscles and support bodily functions.
- Fats: Provide a concentrated source of energy necessary for active puppies. Healthy fats, including Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, are crucial for brain development, skin health, and joint function.
- Carbohydrates: While less critical than proteins and fats, carbohydrates provide energy and support digestive health. Opt for complex carbs like grains and vegetables for sustained energy release.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Essential for various physiological functions, including bone development, immune response, and overall metabolic health. Key vitamins and minerals for puppies include calcium, phosphorus, vitamin A, vitamin D, and potassium.
Feeding Guidelines by Age and Weight:
To ensure proper nutrition, it’s important to follow feeding guidelines tailored to your puppy’s age and weight. Here is a general breakdown:
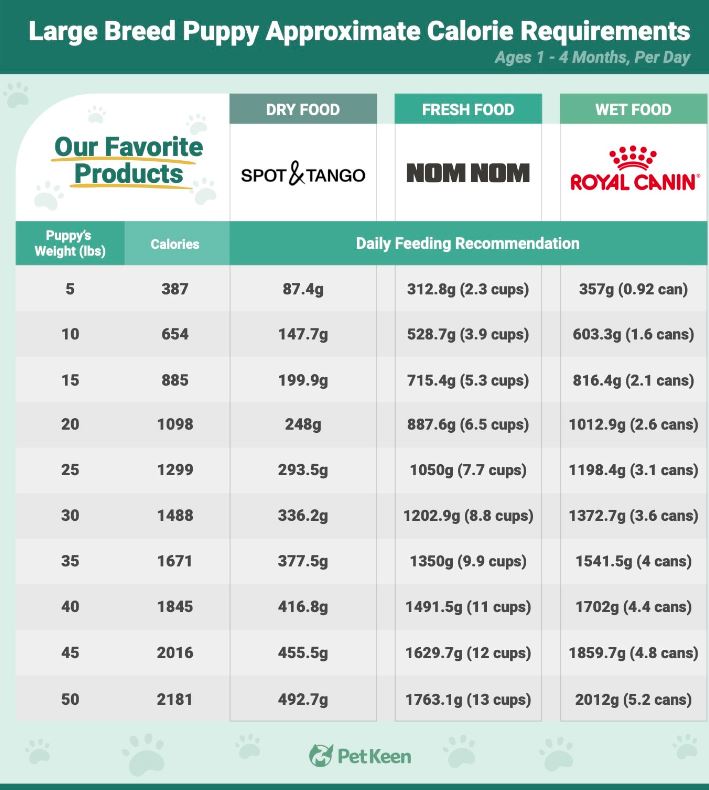
- 2-4 months: Puppies should receive 7/8 to 1 1/8 cups of food per day, divided into four meals. Their weight typically ranges from 15-18 lbs (7-8 kg).
- 4-6 months: Increase the food quantity to 1 1/8 to 1 3/8 cups per day, split into three meals. Weight ranges from 24-26 lbs (11-12 kg).
- 6-12 months: Provide 1 1/2 to 2 cups of food per day, divided into two meals. Weight ranges from 50-60 lbs (23-27 kg).
Adjusting Based on Growth and Body Condition:
While these guidelines provide a baseline, it’s essential to adjust portions based on your puppy’s growth and body condition. Regularly monitor their weight and body condition score to ensure they are neither underweight nor overweight. Your veterinarian can provide guidance on appropriate portion sizes and feeding frequencies to maintain a healthy growth rate.
By understanding and adhering to these nutritional needs and guidelines, you can help your Labrador Retriever puppy grow into a healthy, active adult, ready to enjoy a full and vibrant life.
Maintaining Your Labrador Puppy’s Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight for your Labrador puppy is crucial to ensuring their long-term health and preventing numerous health issues associated with obesity. This section provides a detailed look at the growth stages, feeding guidelines by age and weight, and how to make adjustments based on your puppy’s growth and body condition.
Growth Stages and Nutritional Needs
Labrador puppies go through distinct growth stages, each with unique nutritional needs. Providing the right amount of food and nutrients during these stages is essential for their development and overall health.
Feeding Guidelines by Age and Weight
2-4 Months
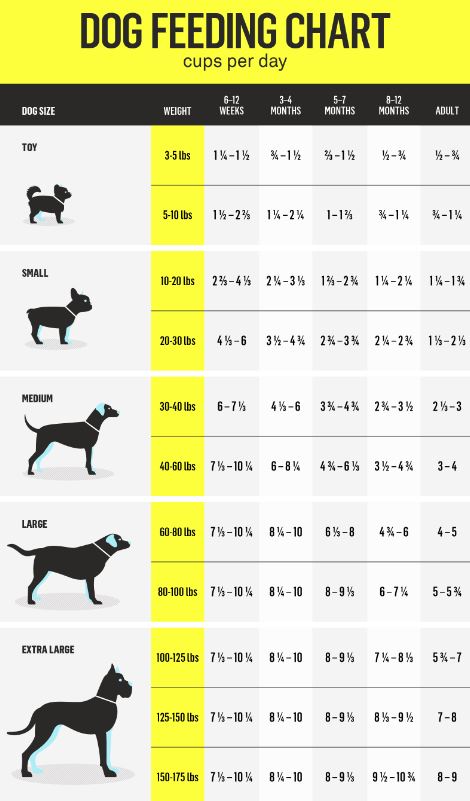
During this stage, Labrador puppies are rapidly growing and require a high-energy diet to support their development. They typically weigh between 15-18 lbs (7-8 kg). The recommended daily food quantity is 7/8 to 1 1/8 cups, divided into four meals. This frequent feeding schedule ensures that their metabolism is supported and their energy levels remain stable throughout the day.
4-6 Months
As puppies grow, their weight increases to approximately 24-26 lbs (11-12 kg). Their daily food intake should be adjusted to 1 1/8 to 1 3/8 cups, split into three meals. This period continues to be one of significant growth, and it is important to monitor their weight to ensure they are developing correctly without becoming overweight.
6-12 Months
Between 6 to 12 months, Labrador puppies’ growth rate starts to slow down, and they typically weigh between 50-60 lbs (23-27 kg). The recommended daily food quantity during this stage is 1 1/2 to 2 cups, divided into two meals. As their growth rate stabilizes, the focus should shift to maintaining a healthy weight and body condition.
Adjustments Based on Growth and Body Condition
While feeding guidelines provide a useful framework, it is crucial to adjust food quantities based on your puppy’s individual growth and body condition. Regularly weigh your puppy and use a body condition scoring chart to assess their health. Adjust portions accordingly to ensure they remain within a healthy weight range.
Body Condition Scoring Chart
The Body Condition Scoring (BCS) chart is an essential tool for monitoring your Labrador puppy’s weight and overall health. It helps determine whether your puppy is underweight, at an ideal weight, or overweight.
Definitions of Underweight, Ideal Weight, and Overweight
- Underweight: Ribs and hip bones are highly visible, and there is minimal fat covering. When viewed from above, the waist appears very pronounced. Underweight puppies may be lacking in energy and have poor coat quality.
- Ideal Weight: Ribs can be felt but not seen, with a slight fat covering. The waist is visible when viewed from above, and the belly tucks up slightly when viewed from the side. Puppies at an ideal weight are energetic and have a healthy coat.
- Overweight: Ribs are difficult to feel under a thick layer of fat. The waist is not visible when viewed from above, and the belly appears rounded when viewed from the side. Overweight puppies may exhibit decreased mobility and have a higher risk of developing health issues.
Associated Health Risks of Being Overweight
Maintaining an ideal weight is vital for preventing the numerous health risks associated with obesity, including:
- Increased Physical Injury: Extra weight puts stress on joints and ligaments, increasing the risk of injuries such as torn ligaments and joint problems.
- Arthritis: Excess weight accelerates the wear and tear on joints, leading to arthritis, a common issue in Labradors.
- Diabetes: Overweight dogs are more prone to developing diabetes due to insulin resistance.
- Reduced Mobility: Obesity can limit a dog’s mobility, making exercise difficult and creating a cycle of weight gain and inactivity.
- Cancer: Studies have shown that obese dogs are at a higher risk of developing certain types of cancer.
- Shortened Life Expectancy: Obesity can reduce a dog’s lifespan by increasing the likelihood of various health issues.
By closely monitoring your Labrador puppy’s weight and adjusting their diet as needed, you can help them maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of obesity-related health problems and ensuring they lead a long, happy, and active life.
Reading and Understanding Puppy Food Labels
Selecting the right food for your Labrador puppy involves more than just picking a popular brand. It’s essential to understand the nutritional components listed on the food labels to ensure your puppy receives a balanced diet that supports their growth and health. This section will guide you through the key elements to look for on puppy food labels and how to evaluate the best brands for your Labrador.

Essential Nutritional Components
When reading puppy food labels, pay close attention to the following essential nutritional components:
Water Intake
Water is vital for your puppy’s overall health. While dry kibble contains about 10% moisture, wet food has much higher water content, sometimes up to 75%. Ensure your puppy has constant access to fresh water to stay hydrated, especially if their diet consists mainly of dry kibble.
Proteins
Proteins are crucial for growth, muscle development, and overall health. Look for high-quality protein sources such as chicken, beef, lamb, or fish listed as the first ingredient. Ideally, puppy food should contain between 22% to 30% protein to support their rapid growth phases.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates provide energy and are important for a balanced diet. Complex carbs, such as brown rice, oats, and sweet potatoes, are preferable as they are easier to digest and offer sustained energy. Carbohydrates should not be the primary ingredient but should be present in moderate amounts to ensure a balanced diet.
Fats
Fats are a concentrated energy source and support brain development, skin health, and joint function. Look for healthy fats like Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, which can be derived from sources such as fish oil and flaxseed. Puppy food should contain about 10% to 25% fat.
Vitamins & Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are essential for various physiological functions, including bone development, immune response, and overall metabolic health. Key vitamins and minerals to look for include:
- Vitamin A: Supports vision and immune function.
- Vitamin D: Crucial for calcium absorption and bone health.
- Vitamin E: An antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage.
- Calcium and Phosphorus: Important for strong bones and teeth.
- Potassium: Supports heart health and muscle function.
- Iron: Essential for red blood cell production.
Supplements
Certain supplements can be beneficial, particularly for breeds like Labradors that are prone to joint issues. Look for foods that include:
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin: These support joint health and can help prevent conditions like hip dysplasia and arthritis.
- Probiotics: Aid in digestion and maintain a healthy gut flora.
How to Evaluate Puppy Food Brands
Not all puppy food brands are created equal. To ensure you are choosing the best food for your Labrador puppy, consider the following guidelines:
Key Nutritional Thresholds
Evaluate the nutritional content against the established guidelines for protein, fat, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Look for foods that meet the nutritional adequacy statements by the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO). These statements indicate that the food provides complete and balanced nutrition for growing puppies.
Ingredient Quality
High-quality ingredients should be at the top of the ingredient list. Avoid foods that list vague terms like “meat by-products” or “animal fat.” Instead, opt for specific sources like “chicken meal” or “beef fat.” Additionally, avoid foods with excessive fillers, artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives.
Transparency and Recalls
Research the brand’s history for transparency in sourcing and production. Brands that openly share information about their ingredient sources and manufacturing processes are generally more trustworthy. Check for any recalls related to the brand to ensure its safety and reliability.
Working with Breeders and Veterinarians
Consulting with breeders and veterinarians can provide valuable insights into your puppy’s specific nutritional needs. Breeders often have experience with what works best for their lines, while veterinarians can offer professional advice tailored to your puppy’s health status.
- Breeders: They can recommend brands and feeding practices based on their knowledge of the breed and their own breeding experience.
- Veterinarians: They can provide dietary recommendations based on your puppy’s health assessments, ensuring any special dietary needs are met.
By understanding and carefully evaluating the nutritional components and quality of puppy food, you can make informed choices that support the health and development of your Labrador Retriever. This proactive approach will help ensure that your puppy receives the best possible nutrition, laying a strong foundation for a healthy, active life.
The Balance in Diet
A balanced diet is crucial for the healthy growth and development of Labrador puppies. It ensures that they receive all the essential nutrients in the right proportions. This section explores the role of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals in your puppy’s diet and how to maintain an optimal balance.
Proteins
Importance and Sources
Proteins are fundamental for the growth, development, and repair of body tissues. They provide the essential amino acids that support muscle development, immune function, and overall health. High-quality protein sources include chicken, beef, lamb, fish, and eggs. These should be the primary ingredients in your puppy’s food.
Ideal Protein Levels for Puppies vs. Adults
Puppies require higher protein levels than adult dogs to support their rapid growth and development. For Labrador puppies, protein should constitute 22% to 30% of their diet. In contrast, adult Labradors need around 18% to 25% protein. Ensuring the right protein levels helps in building strong muscles and maintaining overall health.
Fats
Role of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Fats are a concentrated energy source essential for brain development, healthy skin, and a shiny coat. Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids play a vital role in reducing inflammation, supporting cognitive function, and promoting cardiovascular health. Sources of these healthy fats include fish oil, flaxseed oil, and poultry fat.
Optimal Fat Content
For Labrador puppies, the diet should contain about 10% to 25% fat. This range ensures they get enough energy for growth and activity without contributing to unhealthy weight gain. Monitoring the fat content helps maintain the correct protein-to-fat ratio, which is critical for a balanced diet.
Carbohydrates
Types and Benefits
Carbohydrates provide energy and aid in digestive health. They can be sourced from grains, vegetables, and fruits. Complex carbohydrates, such as brown rice, oats, and sweet potatoes, are preferable as they release energy slowly and are easier to digest.
Balance with Proteins and Fats
While proteins and fats are more crucial, carbohydrates still play a significant role in a balanced diet. They should be included in moderate amounts to ensure energy levels are sustained. Typically, carbohydrates should make up around 30% to 50% of the diet, depending on the individual puppy’s needs and activity levels.
Vitamins and Minerals
Essential Vitamins for Growth and Health
Vitamins and minerals are necessary for various bodily functions, including bone development, immune response, and overall metabolism. Essential vitamins and minerals for Labrador puppies include:
- Vitamin A: Supports vision and immune function.
- Vitamin D: Crucial for calcium absorption and bone health.
- Vitamin E: An antioxidant that protects cells from damage.
- Calcium and Phosphorus: Important for strong bones and teeth.
- Potassium: Supports heart health and muscle function.
- Iron: Essential for red blood cell production.
Common Deficiencies and Their Impact
A lack of essential vitamins and minerals can lead to various health issues. For example:
- Vitamin A Deficiency: Can cause vision problems and weakened immune response.
- Vitamin D Deficiency: Leads to poor bone development and growth issues.
- Vitamin E Deficiency: Results in muscle weakness and reproductive problems.
- Calcium and Phosphorus Deficiency: Causes weak bones, dental problems, and growth retardation.
- Potassium Deficiency: Can lead to heart problems and muscle weakness.
- Iron Deficiency: Results in anemia, characterized by fatigue and weakness.
Ensuring your Labrador puppy’s diet is rich in these essential vitamins and minerals is critical for preventing deficiencies and promoting overall health.
In summary, maintaining a balanced diet for your Labrador puppy involves providing the right amounts of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. By doing so, you support their growth, development, and long-term health, ensuring they lead a vibrant and active life.
Supplements for Labrador Puppies
Supplements can play a crucial role in the health and development of Labrador puppies, particularly for supporting joint health and preventing common breed-specific issues. This section focuses on two key supplements: glucosamine and chondroitin, their benefits, and their importance in the early development of Labrador puppies.

Glucosamine & Chondroitin
Benefits for Joint Health
Glucosamine and chondroitin are naturally occurring compounds found in the cartilage of animals. They are essential for maintaining the integrity of joints and connective tissues. In Labrador puppies, these supplements can provide several benefits:
- Cartilage Support: Glucosamine helps in the formation and repair of cartilage, the tough tissue that cushions joints. Chondroitin sulfate helps maintain cartilage elasticity and prevents its breakdown.
- Reduced Inflammation: Both glucosamine and chondroitin have anti-inflammatory properties, which can reduce joint pain and swelling, promoting greater comfort and mobility for your puppy.
- Improved Mobility: By maintaining healthy cartilage and reducing inflammation, these supplements help improve joint function, allowing for better movement and physical activity.
Importance in Early Development
Labrador Retrievers are prone to various joint issues, including hip dysplasia and osteoarthritis, due to their genetic predisposition and active lifestyle. Early supplementation with glucosamine and chondroitin can be particularly beneficial for preventing these conditions and promoting overall joint health.
- Preventing Hip Dysplasia: Hip dysplasia is a common hereditary condition in Labradors where the hip joint doesn’t fit into the hip socket properly. This can lead to arthritis and pain. Supplementing with glucosamine and chondroitin from a young age can help support the development of healthy joints, potentially reducing the risk of hip dysplasia.
- Supporting Rapid Growth: Labrador puppies grow rapidly, and their joints and bones are under significant stress during this period. Ensuring they have adequate glucosamine and chondroitin can help support their developing skeletal structure and reduce the risk of future joint problems.
- Enhancing Recovery: Active puppies are prone to minor injuries from running and playing. These supplements can aid in faster recovery by promoting cartilage repair and reducing inflammation, ensuring that your puppy can continue to enjoy an active lifestyle without long-term damage.
Dosage and Administration
It’s important to consult with your veterinarian before starting any supplement regimen for your puppy. They can recommend the appropriate dosage based on your puppy’s specific needs and health status. Generally, glucosamine and chondroitin supplements are available in various forms, including chewable tablets, powders, and liquids, making them easy to administer.
- Chewable Tablets: These are often flavored to be palatable to dogs and can be given as treats or mixed with their regular food.
- Powders: These can be sprinkled over your puppy’s food and are an easy way to ensure they receive the supplement consistently.
- Liquids: Liquid forms can be added to food or water and are absorbed quickly, providing fast relief from joint discomfort.
Choosing the Right Supplement
When selecting a glucosamine and chondroitin supplement for your Labrador puppy, look for high-quality products that are specifically formulated for dogs. Check the label for the source and concentration of the active ingredients to ensure your puppy is receiving an effective dose. Products that also contain additional ingredients like MSM (methylsulfonylmethane) can provide extra joint support.
Long-Term Benefits
Starting glucosamine and chondroitin supplementation early in your Labrador puppy’s life can have long-term benefits, including:
- Reduced Risk of Arthritis: By maintaining healthy cartilage and joint function, these supplements can help prevent the onset of arthritis as your dog ages.
- Improved Quality of Life: Healthy joints contribute to overall mobility and comfort, allowing your Labrador to stay active and enjoy a higher quality of life throughout their years.
- Enhanced Longevity: By preventing joint issues and reducing pain, you can help ensure your Labrador lives a longer, healthier, and more active life.
In conclusion, glucosamine and chondroitin are valuable supplements for supporting the joint health of Labrador puppies. By integrating these supplements into your puppy’s diet early on, you can help prevent common joint problems and promote a lifetime of healthy, pain-free movement.
Controversies and Considerations in Dog Food Choices
Choosing the right food for your Labrador puppy can be challenging due to the numerous options and varying opinions on what constitutes a healthy diet. Two popular yet controversial dietary choices are grain-free diets and the BARF (Biologically Appropriate Raw Food) diet. Understanding the potential risks, benefits, and considerations associated with these diets can help you make informed decisions for your puppy’s health.

Grain-Free Diets
Potential Risks and FDA Investigations
Grain-free diets have gained popularity in recent years, driven by the belief that grains are unhealthy for dogs. These diets typically replace grains with legumes, potatoes, and other carbohydrate sources. However, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has raised concerns about a potential link between grain-free diets and canine dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), a serious heart condition.
The FDA’s investigations revealed that many cases of DCM were reported in dogs consuming grain-free diets. While the exact cause is still under study, the potential connection has prompted veterinarians and pet owners to reconsider the necessity and safety of grain-free diets. The concern is that some grain replacements, such as peas, lentils, and chickpeas, may interfere with the absorption of essential nutrients critical for heart health.
The Balance of Ingredients
A balanced diet is crucial for a dog’s health, regardless of whether it includes grains. When evaluating dog food, focus on the overall nutritional content rather than the absence or presence of specific ingredients. High-quality dog foods, whether grain-free or grain-inclusive, should provide a balanced mix of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. The key is to choose a diet that meets the nutritional requirements established by organizations like the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO).
BARF (Biologically Appropriate Raw Food) Diet
Overview of BARF
The BARF diet emphasizes feeding dogs raw, unprocessed foods that closely mimic their natural diet. This includes raw meat, bones, fruits, vegetables, and sometimes eggs and dairy. Proponents of the BARF diet argue that it provides a more natural and nutritionally superior alternative to commercial dog foods, promoting better overall health and vitality.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Improved Coat and Skin Health: Many dog owners report shinier coats and healthier skin in dogs fed a raw diet.
- Dental Health: Chewing raw bones can help keep teeth clean and gums healthy.
- Increased Energy Levels: Some dogs show improved energy and vitality on a raw diet.
- Reduced Allergies: Raw diets can help alleviate food allergies and sensitivities in some dogs.
Cons:
- Nutritional Imbalance: Without careful planning, raw diets can be deficient in essential nutrients, leading to health problems.
- Risk of Pathogens: Raw meat can carry harmful bacteria like Salmonella and E. coli, posing risks to both dogs and humans.
- Time-Consuming and Costly: Preparing a balanced raw diet requires significant time, effort, and financial investment.
Preparation and Safety Considerations
If you choose to feed your Labrador puppy a BARF diet, it is crucial to follow strict safety and preparation guidelines to minimize health risks:
- Source Quality Ingredients: Use high-quality, fresh ingredients from reputable sources to reduce the risk of contamination.
- Balance the Diet: Ensure the diet includes a variety of protein sources, bones, and plant-based ingredients to provide a comprehensive range of nutrients.
- Hygiene Practices: Maintain strict hygiene practices when handling raw meat. Clean preparation surfaces, utensils, and feeding bowls thoroughly to prevent bacterial contamination.
- Consult with Experts: Work with a veterinarian or a canine nutritionist to develop a balanced raw diet plan tailored to your puppy’s specific needs. Regular health check-ups can help monitor your dog’s condition and adjust the diet as needed.
In conclusion, while grain-free diets and the BARF diet offer potential benefits, they also come with significant considerations and risks. The choice of diet should be based on careful evaluation of your Labrador puppy’s nutritional needs, potential health risks, and the feasibility of maintaining a balanced and safe feeding regimen. Always consult with a veterinarian before making significant changes to your puppy’s diet to ensure it supports their health and well-being.
Types of Puppy Food
Choosing the right type of food for your Labrador puppy is crucial for their growth, health, and overall well-being. This section explores the different types of puppy food—kibble, wet food, and raw food—highlighting their advantages, disadvantages, and key considerations.

Kibble
Advantages and Disadvantages
Kibble, or dry food, is one of the most popular choices for feeding puppies due to its convenience and nutritional benefits.
Advantages:
- Convenience: Kibble is easy to store, measure, and serve. It has a long shelf life and doesn’t require refrigeration.
- Dental Health: The hard texture of kibble helps clean your puppy’s teeth by reducing plaque and tartar buildup.
- Cost-Effective: Generally, kibble is more affordable than wet or raw food, especially when purchased in bulk.
- Balanced Nutrition: High-quality kibble is formulated to provide a balanced diet with the right mix of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.
Disadvantages:
- Less Palatable: Some puppies may find kibble less appetizing compared to wet or raw food.
- Dehydration Risk: Kibble contains less moisture, so it’s essential to ensure your puppy has constant access to fresh water.
How to Choose Quality Kibble
When selecting kibble for your Labrador puppy, look for the following:
- High-Quality Ingredients: The first ingredient should be a high-quality protein source like chicken, beef, or fish. Avoid kibble with fillers such as corn, wheat, and soy.
- Nutritional Balance: Ensure the kibble meets AAFCO standards for balanced nutrition. Check for essential nutrients like Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals.
- Age-Appropriate Formulation: Choose kibble specifically formulated for puppies to support their growth and development.
- Brand Reputation: Opt for reputable brands known for quality and safety standards.
Wet Food
Benefits and Limitations
Wet food, or canned food, offers several benefits but also comes with some limitations.
Benefits:
- Palatability: Wet food is often more appealing to puppies due to its aroma and texture, making it a good option for picky eaters.
- Hydration: With high moisture content, wet food helps keep your puppy hydrated.
- Easy Transition: Wet food can be easier for young puppies to eat, especially when transitioning from mother’s milk or a weaning formula.
Limitations:
- Storage: Wet food requires refrigeration after opening and has a shorter shelf life compared to kibble.
- Cost: It is generally more expensive than kibble.
- Dental Health: Wet food does not provide the same dental benefits as kibble and may contribute to plaque buildup.
Transitioning from Wet to Dry Food
To transition your puppy from wet to dry food, follow these steps:
- Gradual Mixing: Start by mixing a small amount of kibble with wet food, gradually increasing the kibble proportion over 7-10 days.
- Monitoring: Observe your puppy’s reaction to the new texture and ensure they are eating well.
- Hydration: Ensure your puppy has access to fresh water as they adjust to the lower moisture content in kibble.
Raw Food
Benefits and Risks
Raw food diets, also known as BARF (Biologically Appropriate Raw Food) diets, consist of uncooked meat, bones, fruits, and vegetables.
Benefits:
- Natural Diet: Advocates argue that raw diets are more natural and better aligned with a dog’s ancestral eating habits.
- Improved Coat and Skin: Many owners report shinier coats and healthier skin.
- Dental Health: Chewing raw bones can help clean teeth and strengthen gums.
Risks:
- Nutritional Imbalance: Without careful planning, raw diets can lack essential nutrients, leading to health issues.
- Pathogen Risk: Raw meat can carry harmful bacteria like Salmonella and E. coli, posing health risks to both puppies and humans.
- Time and Cost: Preparing a balanced raw diet can be time-consuming and expensive.
Handling and Preparation Guidelines
If you choose to feed your Labrador puppy a raw diet, follow these guidelines:
- Quality Ingredients: Use high-quality, fresh ingredients from reputable sources to minimize contamination risks.
- Balanced Diet: Ensure the diet includes a variety of protein sources, bones, and plant-based ingredients to meet nutritional needs.
- Hygiene Practices: Maintain strict hygiene when handling raw meat. Clean all preparation surfaces, utensils, and feeding bowls thoroughly to prevent bacterial contamination.
- Consult Experts: Work with a veterinarian or canine nutritionist to develop a balanced raw diet plan tailored to your puppy’s needs.
In conclusion, each type of puppy food—kibble, wet food, and raw food—has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. By understanding these and making informed choices, you can provide your Labrador puppy with the best possible nutrition to support their healthy growth and development.
Recommended Puppy Food Brands
Selecting the right food for your Labrador puppy is crucial for their development, health, and overall well-being. Here are three highly recommended puppy food brands, each known for their high-quality ingredients and balanced nutrition.
Purina Pro Plan Focus Puppy Chicken & Rice Formula
Key Features
Purina Pro Plan Focus Puppy Chicken & Rice Formula is specifically designed to meet the nutritional needs of growing puppies. It offers a balanced diet that supports overall development and health.
- High-Quality Protein: The primary ingredient is real chicken, providing a high-quality source of protein essential for muscle growth and development.
- DHA for Brain and Vision Development: This formula includes DHA from omega-rich fish oil, which is crucial for the brain and vision development of puppies.
- Rich in Antioxidants: Antioxidants are included to support the developing immune system of puppies, helping them to fight off diseases and stay healthy.
- Calcium and Phosphorus: These minerals are present to help build strong bones and teeth, ensuring proper skeletal development.
- Vitamins and Minerals: The formula contains a balanced blend of vitamins and minerals, such as Vitamin A and linoleic acid (an omega-6 fatty acid), to promote healthy skin and a shiny coat.
- Digestibility: The chicken and rice formula is designed to be easily digestible, ensuring that puppies can absorb nutrients efficiently.
Purina Pro Plan Focus is a trusted choice among breeders and veterinarians, making it a reliable option for your Labrador puppy.
Royal Canin Labrador Retriever Puppy Dry Dog Food
Key Features
Royal Canin Labrador Retriever Puppy Dry Dog Food is tailored specifically for the unique needs of Labrador puppies. This breed-specific formula addresses the particular growth and developmental requirements of Labradors.
- Breed-Specific Kibble: The kibble is donut-shaped to encourage chewing, which slows down the eating process and aids in digestion.
- Immune System Support: The formula includes a blend of antioxidants, including vitamin E, to support the development of the puppy’s immune system.
- Healthy Growth: Balanced levels of calcium and phosphorus support healthy bone growth, while precise energy content helps manage the growth rate to prevent excessive weight gain.
- Digestive Health: The inclusion of prebiotics and highly digestible proteins promotes healthy digestion and optimal stool quality.
- Skin and Coat Health: Essential fatty acids like EPA and DHA help maintain healthy skin and a glossy coat, addressing the specific needs of Labradors prone to skin issues.
Royal Canin’s breed-specific approach ensures that Labrador puppies get the tailored nutrition they need to thrive.
Merrick Classic Puppy Recipe
Key Features
Merrick Classic Puppy Recipe is known for its high-quality, natural ingredients and is designed to support the overall health and development of puppies.
- Real Deboned Chicken: The first ingredient is real deboned chicken, providing a high-quality protein source that supports muscle development.
- Ancient Grains: The formula includes a unique blend of ancient grains like quinoa, which support optimal digestion and provide essential nutrients without common allergens like corn, wheat, or soy.
- DHA for Brain Development: The inclusion of DHA supports healthy brain development in growing puppies.
- Omega Fatty Acids: Omega-6 and Omega-3 fatty acids are included to promote healthy skin and a shiny coat.
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin: These ingredients support healthy hips and joints, which is especially important for large breed puppies like Labradors that are prone to joint issues.
- Vitamins and Minerals: A balanced mix of vitamins and minerals ensures comprehensive nutrition, supporting immune health and overall vitality.
Merrick’s focus on natural, high-quality ingredients makes it a favorite among pet owners looking for wholesome, nutritious food for their puppies.
In conclusion, choosing the right puppy food is essential for the growth and health of your Labrador Retriever. Purina Pro Plan Focus Puppy Chicken & Rice Formula, Royal Canin Labrador Retriever Puppy Dry Dog Food, and Merrick Classic Puppy Recipe are all excellent choices that provide balanced nutrition tailored to meet the needs of growing Labrador puppies. By selecting a high-quality puppy food, you can help ensure that your Labrador develops into a healthy, active adult dog.
In conclusion, ensuring your Labrador puppy receives the right nutrition is fundamental to their growth, health, and development. Utilizing a Labrador feeding chart by age is crucial for understanding their specific dietary needs at various life stages, including a balanced intake of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. While this guide provides a solid foundation for understanding puppy nutrition, it’s always beneficial to consult with a veterinarian or a pet nutritionist. These professionals can offer personalized advice based on your Labrador puppy’s specific needs, health status, and developmental stage. They can also help address any dietary concerns or adjustments that may be necessary as your puppy grows. By following these guidelines and working with professionals, you can help ensure your Labrador puppy grows into a healthy, happy adult dog.
Age -Jonah Beres age A Comprehensive Exploration of His Life and Career
Understanding the Legal Drinking Age in Punta Cana, Dominican Republic A Comprehensive Guide for Travelers
Discover DannyLux Age and His Journey from TikTok Star to Pop Sensation
Comprehensive Analysis of Yu-Gi-Oh!’s Age of Overlord card list A Deep Dive into the Latest Core Booster Set
Understanding Sexual Health Education The Age of Consent in WA State and Support for Rape Victims
Unveiling Luke Beasley Age and Its Impact on His Basketball Career An In-Depth Analysis
Understanding the Age of Consent for Indiana Legal Implications and Consequences